You have a new product and you think you're ready to get customers. Before doing anything else, your product launch needs to carefully follow a go-to-market strategy framework to optimize market pull by attracting the right buyers.
That's the way successful product launches accelerate product-market fit and mature products can find new customers.
This go to market strategy framework, proven in over +200 high-tech projects and based on the behavioral science of how humans buy tech products (The innovation-adoption lifecycle), will help you develop your market and help your audience buy, adopt and diffuse your product successfully.
I'm going to walk you through the step-by-step process to design a successful go to market strategy, including the next contents:
- What is a go-to-market strategy?
- When do you need a go-to-market strategy?
- Who is responsible for the go-to-market strategy?
- How to build a go-to-market strategy?
- Go-to-Market strategy framework

What is a Go-to-Market (GTM) strategy?
A go to market strategy is a step-by-step plan that business leaders, founders, and innovators use to bring a product to market or launch an existing product in a new market.
An effective go-to-market strategy includes steps to discover the right market for new products, understanding what customers want to buy, defining how to stand out from competitors, aligning with business objectives, and positioning the product as a differentiated solution during the product launch or introduction process.
When do you need a Go-to-Market strategy?
If you're in any of the following situations, thinking about your go-to-market strategy is critical to gain traction or accelerate growth successfully:
- To introduce an existing product into a new market.
- To launch a new product in an existing market or when you are expanding to a new market.
- When your sales are stalling, reaching a growth plateau, or sales cycles are longer than they used to be. (Diagnose where your pipeline is breaking.)
- When there is a lack of success in the customer segment.
- When the competitive environment or market conditions are changing.
That being said, a go-to-market strategy must continuously evolve to align with the constant changes in your buyer behavior as your market matures.
Who is responsible for the Go-to-Market strategy?
It depends on the product phase and the size and structure of a company:
- In startups launching new products, the founder or CEO must lead the go-to-market strategy.
- In mature companies launching new products, a dedicated product marketer or a CMO with exclusive dedication to innovation must lead the initiative. This designated leader must differ from the product manager or owner to bring the market perspective to the table versus the engineering or product view.
- In mature companies with mature products, the product marketing director takes care of some of the components like research and messaging. The distribution efforts are the responsibility of revenue, marketing, and partnerships teams. The positioning strategy must always be a CEO-led strategy as it is the most influential strategic decision for long-term success.
How to build a Go-to-Market strategy?
To create a go-to-market strategy follow these steps:
- Select the right target market: problem to solve + audience
- Understand your target's motivations to buy
- Analyze your competitors to differentiate
- Discover potential next target markets
- Design a low-risk value proposition and offering
- Create a product positioning and messaging that resonates
- Identify market ecosystem partners and alliances
- Strategize distribution channels
- Test your customer's willingness to pay and pricing strategy
- Plan and execute the launch sequence and tactics
- Align your product, product marketing, marketing and sales teams
This go to market strategy framework is a step-by-step plan based on our observations launching +200 high-tech products by following the behavioral science of The Technology Adoption Lifecycle (how humans react to innovations and new things).
Let's dig into the details of the go-to-market strategy framework!
11-Steps Go-to-Market strategy framework
1. How to select the right target market
The first step to developing a go-to-market strategy is to select the right combination of problem to solve and audience to target by researching markets. This step validates and prioritizes potential industries and buyers and/or uses cases to target first and accelerate product-market fit before spending money on an innovation nobody wants.
The question to answer is who your early customers could be. You'll be looking for customers who are excited about your innovation and willing to pay to try it first. If you create a new market, these first customers will fall into the psychographic profile of innovators and early adopters.
Your resources are limited, and the strength to win a segment (market) over your competitors is determined by how focused your go-to-market strategy is on a segment. That's why we strongly encourage you to discover a specific early customer excited about your product.
That's why it is also called the beachhead segment. Once you win customers into this first target, you can sell into an adjacent segment from a more credible market position (with testimonials, cases and experience).
This is the most critical step to building an effective gtm strategy, as the other steps depend on selecting the right market to target.
Unlike popular beliefs, we have observed that market size is not the most profitable way to assess opportunities. There are nine other critical factors to evaluate the potential success of launching a product. The top market opportunities are located in the middle of 3 dimensions:
- Ease of buying factors — how willing is the market to purchase your product now?
- Ease of selling factors — how ready is your selling side to win the opportunity?
- Organizational effectiveness factors — how ready is your organization to build a strong market position by starting with this opportunity?

As you gather feedback and learn from the market, answer the next questions. Then score from 1 to 5 the questions for each combination of industry + use case you can potentially target.
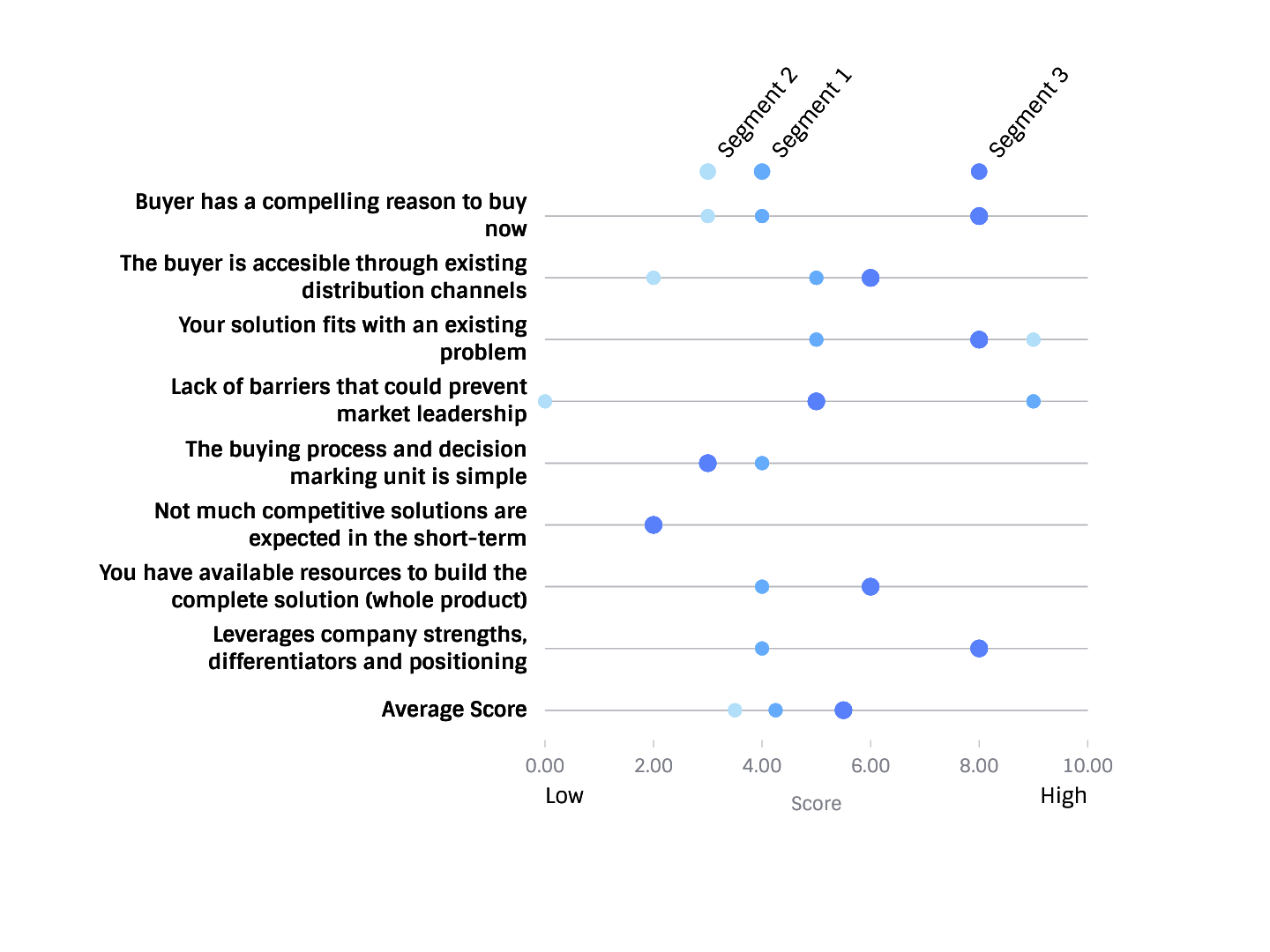
Once you have analyzed the opportunities and scored them, you'll clearly understand who to target first to bring a new product to market.
Answer these questions to score each use case/segment:
- What customers and use cases fit best with your solution or product? Which ones have a compelling reason to buy?
- What segment or use case allows you to have a faster time to market?
- What segment allows you to build a market leadership position faster?
- What segment leverages your company's strengths and differentiators?
- In what segment can you expect fewer competitors in the short term? Why?
- What customer segments or use cases are more accessible through the existing sales channels?
- What is the customer segment or use case where you can develop a complete product offering attributes more quickly?
- What are the barriers to success?
2. How to clarify your target audience's motivations to buy your product
Once you have assessed and selected the right market to target, describe in a detailed way the group of potential early customers that can help you achieve product/market fit faster.
Ensure the target customer has a compelling reason to buy the new product as soon as possible. Describe the specific motivation that your early customers have to buy your product.
In this step, you'll define your buyer's journey and Ideal Customer Profile scenario with their pain points, jobs-to-be-done and desired outcomes.
Design the scenarios of the most promising opportunities by aggregating patterns of step 1. Each scenario or segment must answer most of the following questions:
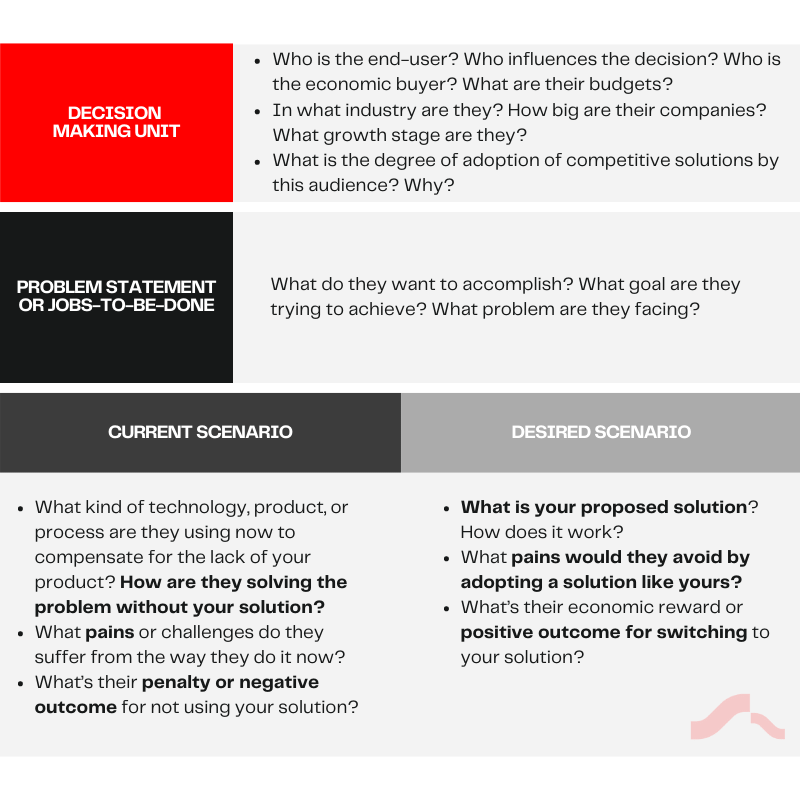
Go-To-Market strategy questions to answer:
- What are your potential targets' industry, size, and geographical boundaries?
- What is the market maturity phase of the market category of your product? Why?
- Who are the target end-users? Who is the Decision Making Unit (DMU) or buying center? Who influences the decision? Who triggers the decision?
- What motivates the target customers (or buyer personas) and end-users to buy your product? What do they want to achieve? What is their Job-To-Be-Done? What is the business value your product unlocks for them?
- What are the target customers struggling with (pains)? What is making them solve that pain right now? What outcomes are they looking for?
- What is your end-user's workflow or customer's journey?
- How and why does your product help potential customers reduce pain, perform the job to be done and achieve the desired outcomes? What is the transformation that your product provides?
- How is your core solution better suited for the target than the competitive alternatives or the compensating behaviors?
3. How to differentiate from competitors
Perform a competitive analysis and identify the "most dangerous" alternative. Analyze their capabilities and look for ways (in addition to trademarks and patents) to develop and maintain a competitive advantage.
Also, think that your toughest competitor might not be a solution but the status quo or risk of changing their current approach (workflow change).
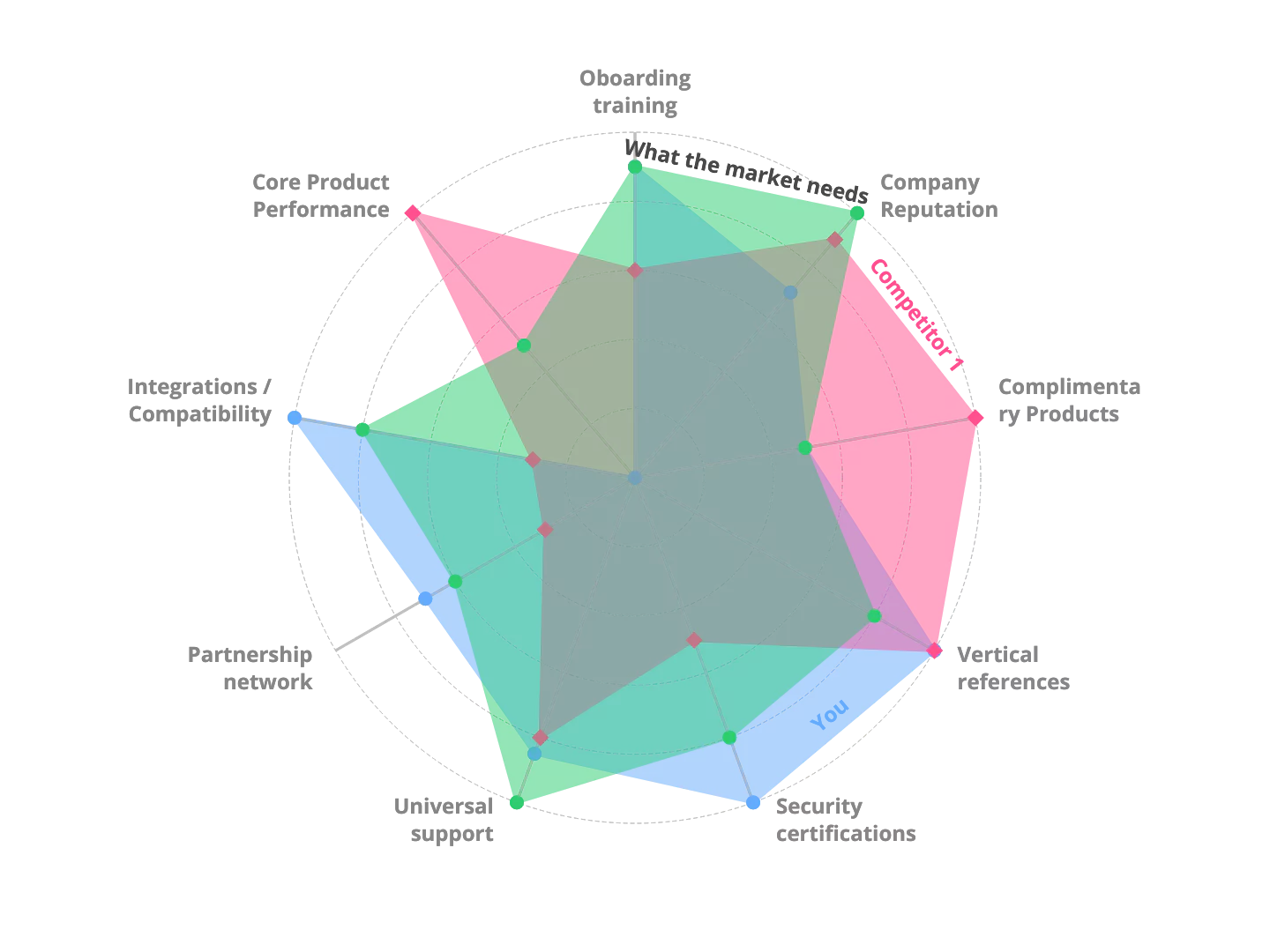
Go-To-Market strategy questions to answer:
- Is there a company or product that overlaps with your intended positioning?
- Are you competing against a solution or change (status quo, adoption frictions, market creation...)?
- What are their strengths and weaknesses? What are the key features that differentiate them?
- Are there competitor whitespaces you can fill in with your core features?
- How are your intangibles differentiating from competitors? What are your competitor's switching costs?
- Is your total cost of ownership better than your competitor's?
4. How to discover next target markets
Identify an adjacent niche market or use case that extends your growth after your early customer segment of step 1.
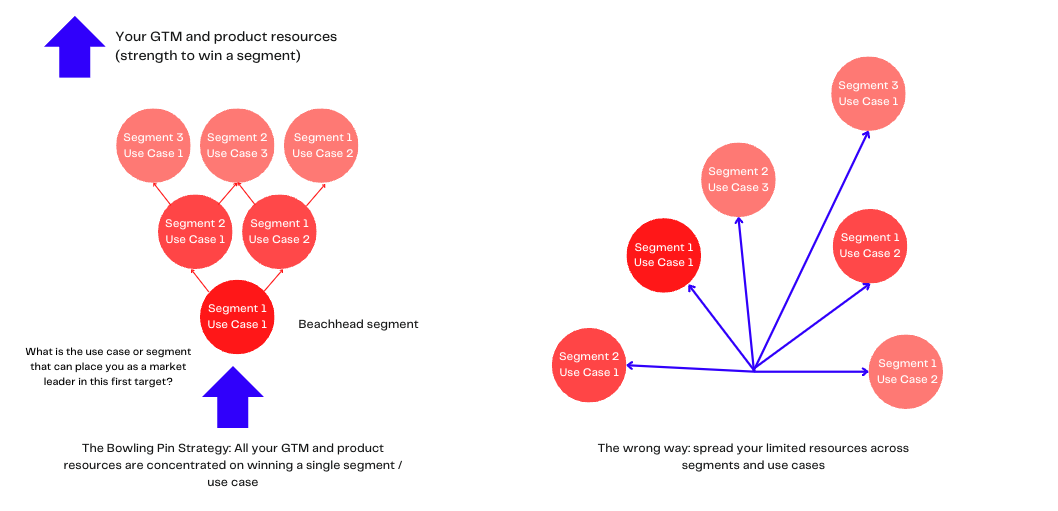
Go-To-Market strategy questions to answer:
- What is the adjacent niche market or use case that extends the growth you make in the initial customer segment?
- What adjacent niche market should we prioritize? Why? How does it fit with your strengths and weaknesses?
5. How to design a low-risk perception value proposition and product offering
This step is one of the two main differentiators of our approach to go-to-market strategy: building a low-risk value proposition and offering so your product can achieve mainstream adoption faster or Cross The Chasm (in the case you're launching a disruptive or discontinuous innovation).
In this step, you determine what makes your value proposition and offering "complete and compelling" in the eyes of the target audience.
A low-risk value proposition comprises a set of features, intangible attributes, and services the target audience requires to achieve their compelling reason to buy and become the lowest-risk choice.
Feel free to use our whole product concept: The Brand Differentiation Wheel™ with the 12 key elements that reduce the risk perception of technology-based products:
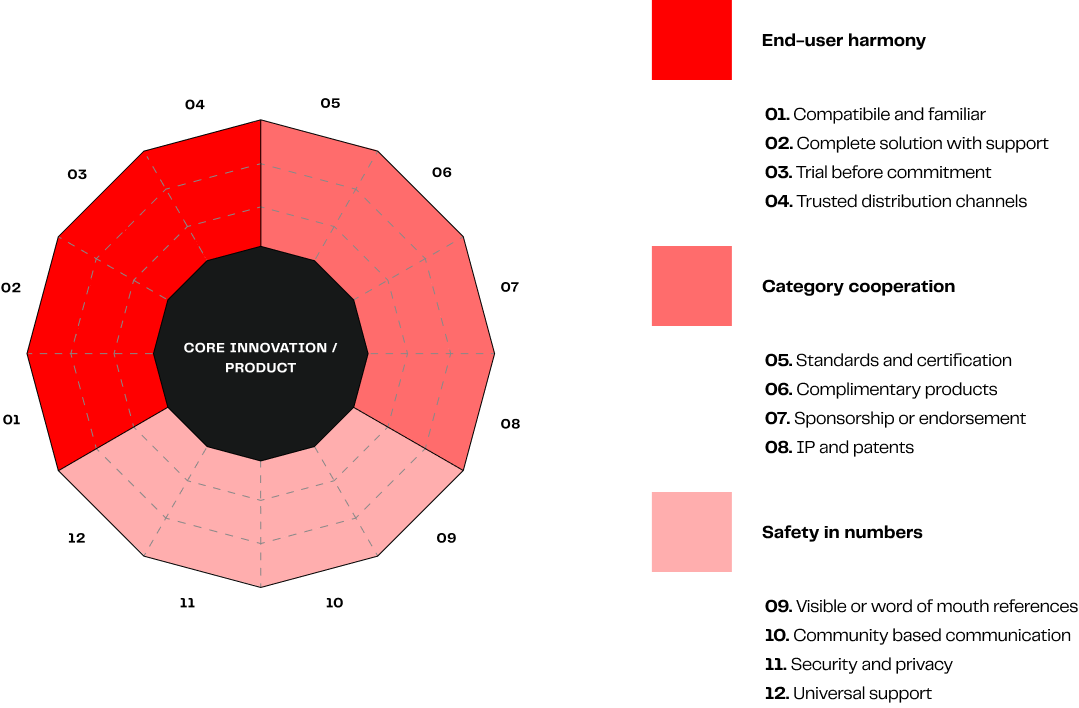
Go-To-Market strategy questions to answer:
- What is a compelling value proposition for our buyers and end-users?
- What should be your product's value proposition?
- What risk-reduction features should we add to your value proposition and offering to convince more buyers? (ex. free trial)
- What do the prospective customers ask about that your company doesn't have or can't provide?
- Who or what else needs to be involved in a project to deliver total value for the end-user (e.g., a sales consulting service, predefined visualizations, integration with other tools, support service...)?
- What does the user or decision-maker complain about? What are the hesitation points we heard from prospective customers?
- What kind of organizational and business model adjustments are needed to accomplish product completeness?
- How would sales approach a proposal of a complete solution? What should be included in the Total Cost of Ownership in your proposals?
- Is now the right time to build a complete and low-risk solution regarding market maturity, or should we focus on building core product features?
- What other tools do the target customer use that complement your product?
6. How to create your positioning messages
After going through all the previous steps, you should clearly understand who your target market is and what pains, struggles and challenges you can solve for them with your product or idea.
Armed with that information, it is time to craft a value proposition and a set of positioning messages that position your new product or innovation as a relevant, differentiated and credible product for your audience. (Strong positioning is critical—weak positioning is often why sales reps fail.)
Proper messaging allows your product and company to be seen as a credible provider for the buyer by addressing different types of concerns.
Your pitch, website and narrative should communicate 4 different types of messages: technology messages, product messages, market messages, and company messages.
It is also critical to communicate the right combination of messages to each layer in your market ecosystem to help them position your product (steps 7 and 10).

Go-To-Market strategy questions to answer:
- By solving this problem for the selected target audience with your innovation idea, are you creating a new market or entering into an existing market?
- What words do prospective customers use to describe the struggles and pains your product is intended to solve?
- What types of messages resonate the most for your target market?
- What competitive strengths and differentiators should you communicate?
- Why do you win or lose deals? What should your positioning and messaging improve to increase conversions and win more?
- What is the right balance regarding positioning messages (technology, product, market, or company)? What kind of messages does the market demand according to the phase of technology adoption?
- How do you combine all those messages into a storytelling and narrative that resonates with your early customers?
7. How to map ecosystem partners and alliances
This is the other main differentiator of our go-to-market strategy approach: build a market ecosystem of partners and alliances to drive credibility for you, support your product validation/launch, and help you create your market.
Every market has a set of ecosystem or infrastructure players between your product/brand and your prospective customers. 10% of the market players in the ecosystem influence the other 90%.
The best way to help the market position your product in a way that highlights your strengths is by leveraging your market ecosystem or infrastructure. Build relationships with the top 10% of players in the ecosystem, address their concerns about your product, and nurture them with custom marketing assets they can share with the rest of the market.
Understanding the market ecosystem forces and building relations with the top 10% of ecosystem influencers is critical to increasing Word-Of-Mouth. Building this WOM system reduces customer acquisition costs, positions your product in the market, builds credibility and brand awareness and optimizes market pull.

In addition, it is difficult to deliver every element of a low-risk product offering from a single organization.
Think about how Microsoft needs its partners to adapt AZURE offerings to the end-user workflows with consulting services.
Usually, the only way to satisfy this market requirement is to identify and recruit the necessary partners and allies. It includes finding the right partners to act as familiar selling channels.
In this step, you must find organizations and map players that:
- Will help you assemble and deliver a low-risk product offering. These could be alliances and partners with other service or product providers.
- Will support your new product launch or go-to-market process. These could be industry associations, consultants, analysts, research firms, thought leaders, journalists...
This step is critical for your market-building strategy, as no B2B tech market exists without this ecosystem of players. If you are one of the first to build and be part of this ecosystem for an emerging market, you'll become a category creator and win the first mover advantage.
By building relationships with your market infrastructure or ecosystem, you can expect the next benefits:
- Amplify reach by incentivizing WOM communications through these influencing players.
- Build brand and product credibility by having these 3rd party players communicate your positioning messages.
- Reduce CAC with a market that knows when to buy from you and why.
- Reduce sales cycles through well-known references.
- Build a lasting advantage with the network effect your market infrastructure creates.
- Validate and improve product and go-to-market strategy.
- With the support of market infrastructure, a market leadership position is easier to achieve.
Go-To-Market strategy questions to answer:
- What are the layers (types of organizations and individuals) that influence the market of your target segment?
- Who are the top 10% of organizations and individuals within each layer of your ecosystem?
- What partners and allies would help make your technology/product more appealing to customers? What partners and allies would help make the solution more complete by adding offering attributes your company can't provide?
- Why should existing or new partners support your product introduction and selling? What would be a compelling, unique value proposition for partners?
- What partners and allies would help amplify your reach and build your market?
- What other partnerships should we leverage to complete your solution, support a product introduction or reintroduction process, improve competitive advantage and drive early customers?
8. How to design your distribution strategy
Identify and prepare the most suitable distribution channels to drive awareness to the market and sell your product. This step could overlap with the last one because you may have identified channel partners.
You can use the next framework to place your new product or innovation in the sliders and understand if you should focus your distribution efforts on marketing tactics or customer relationships (sales or partnerships).
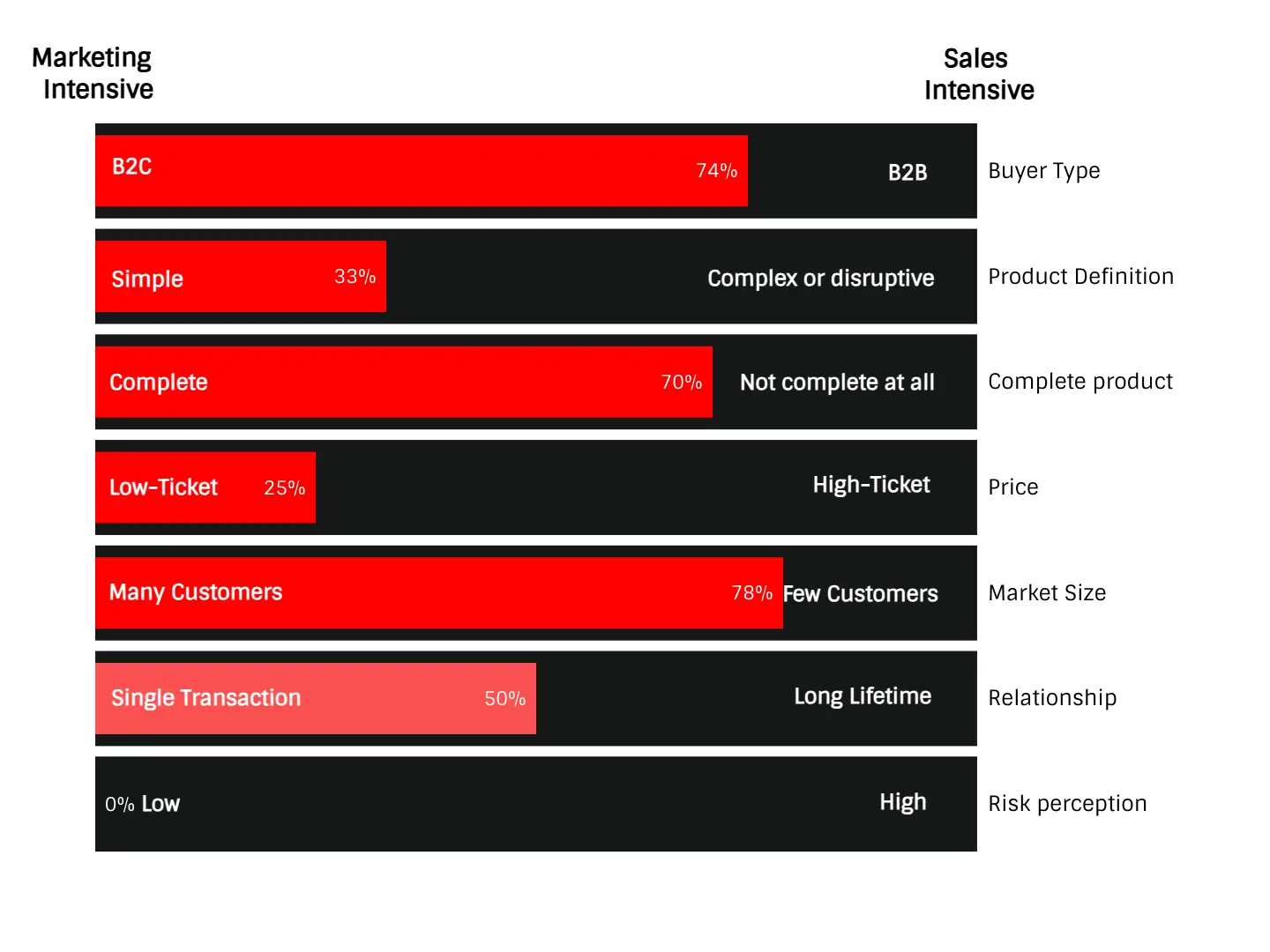
Go-To-Market strategy questions to answer:
- What is the appropriate load of marketing efforts by channel and by stage? Is your solution most suited to focus on a sales-led, marketing-led, partner-led, or product-led growth plan?
- What direct and indirect channels, teams, and individuals should be involved and ready for the launch? (in case of launches)
- Who else should be involved in launching the solution to the infrastructure and maintaining those relationships?
- What marketing channels should we leverage? What does a marketing plan look like for your type of product?
- What should be the sales strategy and sales organization approach to fit the customer needs? How does it affect the direct sales team?
- How should your sales team approach sales enablement to sell a complete solution?
- How should your sales process be adapted to fit your target audience's motivations and risk perception?
- What enablement collaterals do your sales team and partners need to introduce the solution?
9. How to test your customers' willingness to pay and pricing strategy
Help your customer perceive the high value of your product and pay what it's worth. Suppliers, partners, and sales channels must be appropriately rewarded for selling your solution. Your pricing strategy must reflect these requirements.
To get inspired, read the next willingness-to-pay tests you can execute, depending on your go-to-market phase (validation, soft-introduction, general availability...):
Test your value story with your ecosystem and audience
The best way to test the willingness to pay is, well... to sell your product! Depending on the complexity of your product, you can do so by:
- Putting together a landing page with your value story and pricing tiers and conducting a preference test with your target audience.
- Pitching your value story with a deck to your early customers.
- Pitch your value story to potential partners and allies in your ecosystem. Gather their feedback on perceived value and your pricing vs. the pricing of existing alternatives. Gather information about margins that will incentivize their participation as a sales channel.
Conjoint Analysis surveys
Describe and show high-fi screenshots or photos of your prototype to your potential early customers, then survey them.
Conjoint analysis is a highly effective tool for pricing research. It involves breaking down a product into its individual components (features and prices) and creating various configurations for respondents.
By doing this, researchers can determine how price and product features influence customers' willingness to pay.
Van Westendorp Price Sensitivity Meter
The Van Westendorp Price Sensitivity Meter is utilized to establish an acceptable price range for a specific item by asking the following questions:
- At what price would you perceive the product as being too costly to consider?
- At what price would you believe the product is so cheap that it raises doubts about its quality and makes you disregard it?
- At what price would you think the product is becoming expensive but still worth considering?
- At what price would you consider the product a great deal - a worthwhile purchase for your money?
Van Westendorp will produce a set of ranges and an optimal price:
- Lower threshold - the point where "too inexpensive" intersects with "expensive"
- Upper threshold - the point where "too expensive" intersects with "not expensive"
- Optimal price point - the point where "too expensive" intersects with "too inexpensive"
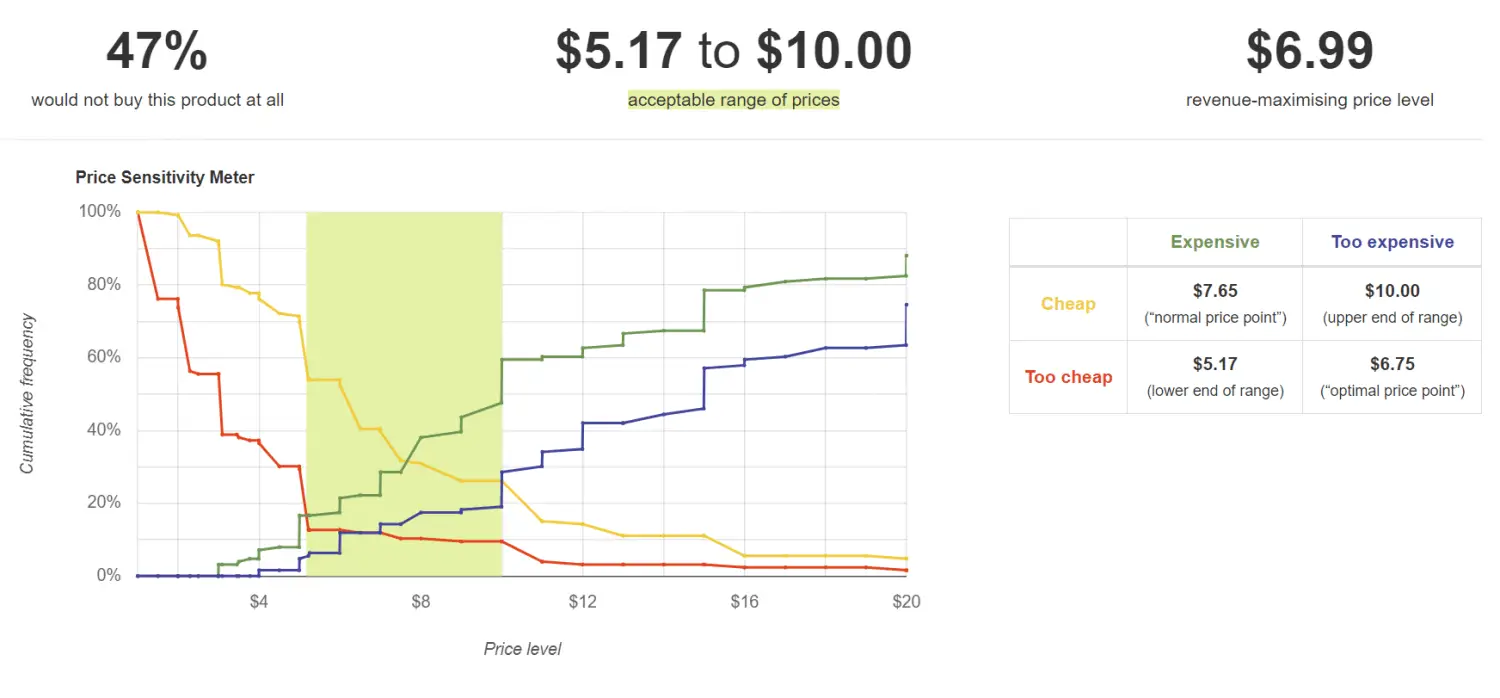
Go-To-Market strategy questions to answer:
- What is the main value driver of your product that can be related to your pricing tiers? For example, if you sell software that identifies leads landing on a website, you can create pricing tiers by the number of leads identified. That way, you can build pricing tiers related to the value delivered and scale as your customers scale.
- What is the pricing that creates a profit margin for you, incentives for your distribution channels, and return on investment for your customers?
- How can you make this a recurrent, steady, and sustainable source of revenue?
- How does this revenue model fit with your current business model?
10. How to create your product launch plan and tactics
By now, you should have a go to market ecosystem map (step 7).
This step will leverage that ecosystem map to build a content marketing strategy and launch activities. The difference is that this content strategy will be focused on distributing the content and key positioning messages in 1:1 conversations with your ecosystem.
Use these steps to introduce your product and build your market:
- (step 7) Map your market infrastructure of players. Follow the pyramid and define the layers and individuals that compose your market infrastructure. Use LinkedIn, Google, and Sparktoro as your tools for this step.
- Research each player.
- Create an outreach and content strategy for each layer in the pyramid.
- Assign an owner to develop a relationship.
- Ask for feedback from the players. Fix their concerns and get back with your fixes in terms of product and messaging.
- Keep the relationship warm. As you develop the relationship, you may want to co-author papers/posts, co-speak at events, go live with them, and contribute to industry reports...
Go-To-Market strategy questions to answer:
- What are the ecosystem perceptions about your industry, market, technology, and innovation?
- How can you best serve their interests in a way that sets up a win-win relationship to support each other's goals? (You give them insider information to support their "influencer" position, and they help you by sharing the information you provide and giving you valuable feedback).
- What kind of collaterals do you need to build to provide the market ecosystem with the different needs of information they have?
- Who will be in charge of keeping alive a market-relations program with all the layers of the ecosystem?
- How else can you leverage the relationships with them? (e.g. statement of support, joining press releases, joint events, building formal partnerships...)
11. How to align your product, sales and marketing teams
Even the best go-to-market strategy framework fails because of a lack of leadership, organizational and company strategy alignment. The bigger your organization, the more complex it is to drive alignment.
A successful product launch factor is to set up a go-to-market strategy or launch committee to ensure team alignment, manage expectations, and follow up on the success metrics.
In established companies, the next example of go-to-market strategy process will help you get closer to a successful product launch.
Go-To-Market strategy questions to answer:
- What teams should we be involved in this go to market plan?
- How do we define "success"? What key performance indicators (or OKRs) will you measure in the short and long term? Are these objectives cross-organizational and committed by all your Go to Market leaders?
- How do we get everyone involved and ensure that all the different Go to Market functions are represented in this plan and agree to pursue it?
- What follow-up process and cadence should you set to meet the expected deadlines and drive organizational alignment toward this gtm strategy objectives?
- How do we ensure that this gtm strategy aligns with the corporate-level strategy? Who should we talk to? What are other corporate-level growth efforts?
- What needs to be in place regarding marketing strategy, sales, and product readiness to launch the solution or accelerate revenue?
- What other business model tweaks should we implement to accelerate the acquisition of new customers and expand the revenue in existing customers? How does it impact the business plan?
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a go-to-market (GTM) strategy and why is it important?
A go-to-market (GTM) strategy is a detailed, step-by-step plan that outlines how a company will bring a product to market, whether it is a new product or an existing product entering a new market. A well-defined GTM strategy is crucial because it provides a roadmap for attracting the right customers, achieving product-market fit, and creating a sustainable competitive advantage. It ensures that all teams, including product, marketing, and sales, are aligned and working towards the same goals, which is essential for a successful product launch and long-term growth.
What are the key components of a comprehensive go-to-market strategy framework?
A comprehensive go-to-market strategy framework consists of several interconnected components that guide the entire process of bringing a product to market. This framework includes selecting the right target market, understanding the motivations of the target audience, analyzing the competitive landscape, designing a compelling value proposition and offering, creating a clear positioning and messaging strategy, identifying key partners and alliances, defining distribution channels, establishing a pricing strategy, planning the launch sequence, and ensuring alignment across all internal teams.
How does the concept of a "beachhead segment" influence a go-to-market strategy?
The concept of a "beachhead segment" is a critical element of a successful go-to-market strategy, particularly for new products or innovations. It refers to the initial, specific, and highly focused target market that a company aims to capture first. By concentrating resources on winning over this initial segment of early adopters, a company can establish a strong market position, gather valuable feedback, and build credibility. Once the beachhead segment is secured, the company can then leverage this success to expand into adjacent markets from a position of strength.
What is the role of behavioral science in the go-to-market strategy framework?
Behavioral science, particularly the Technology Adoption Lifecycle model, plays a foundational role in this go-to-market strategy framework. This model explains how different groups of people react to and adopt new technologies and innovations over time. By understanding the psychological profiles of different adopter groups, from innovators and early adopters to the majority and laggards, a company can tailor its messaging, positioning, and overall strategy to resonate with the specific mindset of its target audience at each stage of the market development process. This behavioral science-based approach helps to create a more effective and persuasive GTM strategy.
About the Author

Jose M Bermejo
Founder @ The Offering Design Co - The Business Potential Strategist
CEOs call me to break revenue ceilings after burning money on ads, funnels, and hirings that did not work. I'm the call that stops the break. 15+ years in the trenches—first as a CRO scaling revenue 120%, now helping B2B CEOs stop selling harder and start selling smarter. Your "strategy" isn't the problem. Your offering is. IESE MBA. Harvard & MIT certified.
LinkedInRelated Articles
How to Build a Go-to-Market Strategy (That Actually Works in 2026)
Learn how to build a go-to-market strategy that works. Skip the 90-day plans—design a Gravity Offering that makes buyers say yes. Free audit.
How to Use the Whole Product Concept to Differentiate Your Product
Discover the Whole Product Concept and how it bridges the gap between early adopters and the mainstream market. Essential for tech marketing success.
What is Product Positioning? Guide, Templates & Examples to Design Your Strategy
Master product positioning with this comprehensive guide. Learn how to define your unique value proposition and stand out in a crowded market.