In this article, I'll introduce you to a fresh version of the whole product concept, a model developed originally by Lee James at Regis McKenna, an later popularized in the book Crossing The Chasm.
I've been working during the last few years with Warren Schirtzinger, ex-colleague of Lee James and the guy who coined The Chasm to continue developing this model. With this new version of the Whole Product, we aim to guide CXOs in high-tech to understand the buyer's needs and align their business strategy to those needs to become highly differentiated brands, and achieve status of "the go-to solution" in their market.
What is the whole product concept?
The "whole product concept" refers to the complete package that a customer receives, not only physical but perceptional when they purchase a product or service. It includes not just the physical product, but also any additional features, services, customer service, and overall customer experience that accompany it to make the "core product" more buyable in the perception of the customer.
As the technology markets mature by following the Technology Adoption Lifecycle curve, the buyers' motivation changes, and product offering intangibles assume more importance than the core product's features and technology.
Often, new successful products lose their initial traction because a new entrant or even an incumbent is more successful positioning its product based on a more effective mix of intangibles attributes rather than technology or core product features — even if the second product is not technically superior.

The whole product concept recognizes this need for intangible elements to complete the offering for most potential buyers by adding new dimensions that surrender the core product or technology.
The intangible dimensions are the ones that help technology products and innovations differentiate and win beyond the early adopters or past product/market fit. They allow the customer to avoid painful disruptions and reduce risks while adopting and making buying decisions about tech products.
Those are the foundations of the augmented or whole product model, largely refined since 1983, when Theodore Levitt introduced it when working at Regis McKenna. Almost a decade later, Geoffrey Moore popularized the model in his book "Crossing the Chasm".
What innovators and early adopters want
When introducing a new product, or innovative technology, the core product features (generic product) are all that matter to convince innovators and early adopters — the technology enthusiasts leading the adoption of innovations and technologies.
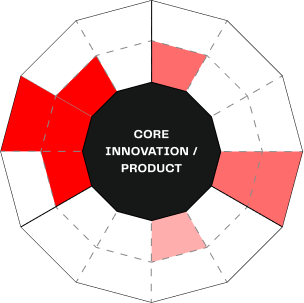
The above illustration shows the mix of product offering tangibles (core innovation/product) like features, and intangibles (surrounding the core, colored) for the early adopters. Notice how the buckets surrounding the core innovation are not very colored, and the core innovation is a big part of the complete product mix.
The bad news is that innovators and early adopters who care about technology and features are only 16% of any given technology market.
Introducing the Brand Differentiation Wheel™, an updated version of the whole product concept
Our team has been researching and learning over +200 consulting projects to refine the whole product concept in order to understand the key drivers in technology/innovation decision-making. We have observed and confirmed that the key buying objective for most potential buyers of an innovation or technology is to feel safe.
Have you ever heard decision-makers not buying from a startup because they are afraid of becoming technology orphans or concerned about customer support, onboarding, or change management? They buy from the biggest guy in the market because "nobody was ever fired because of hiring IBM".
That's what the 84% of potential buyers —the mainstream market— want: to feel safe to buy an innovation or technology. The are early-majority and late-majority, and are not motivated to buy a new cool tech, but to solve a problem and make a small improvement within its company, avoiding disruption and risks.
This sudden change in the motivations to buy and key decision drivers is what we anticipate with our improved version of the whole product concept framework: The Brand Differentiation Wheel™.
No, prospective customers in the mainstream don't care just about your value proposition.
The Brand Differentiation Wheel™ illustrates how the 12 value drivers and expected offerings change from an early market to a mainstream market — where sustainable, profitable growth lies.
Most new technology products fail to break growth plateaus or reduce sales cycles past product-market fit because go-to-market leaders fail to understand the safety needs that their next wave of product adopters have. That next wave of prospective buyers, will no longer technology enthusiasts and visionaries.
We see over and over again business and marketing managers neglecting to adjust their strategic positioning and marketing strategy to adapt to the new key selling points. After the product-market fit, it's time to transition from a product positioning to a brand-based positioning based intangibles rather than focus exclusively on core product features .
This update on the total product concept was introduced for the first time by our Sr. Partner Warren Schirtzinger. He named it "The Low Risk Recipe™" because selling to mainstream buyers is all about lowering the risk perception of your product.
The 12 elements are, in essence, attributes that reduce the risk perception of your core technology or product:
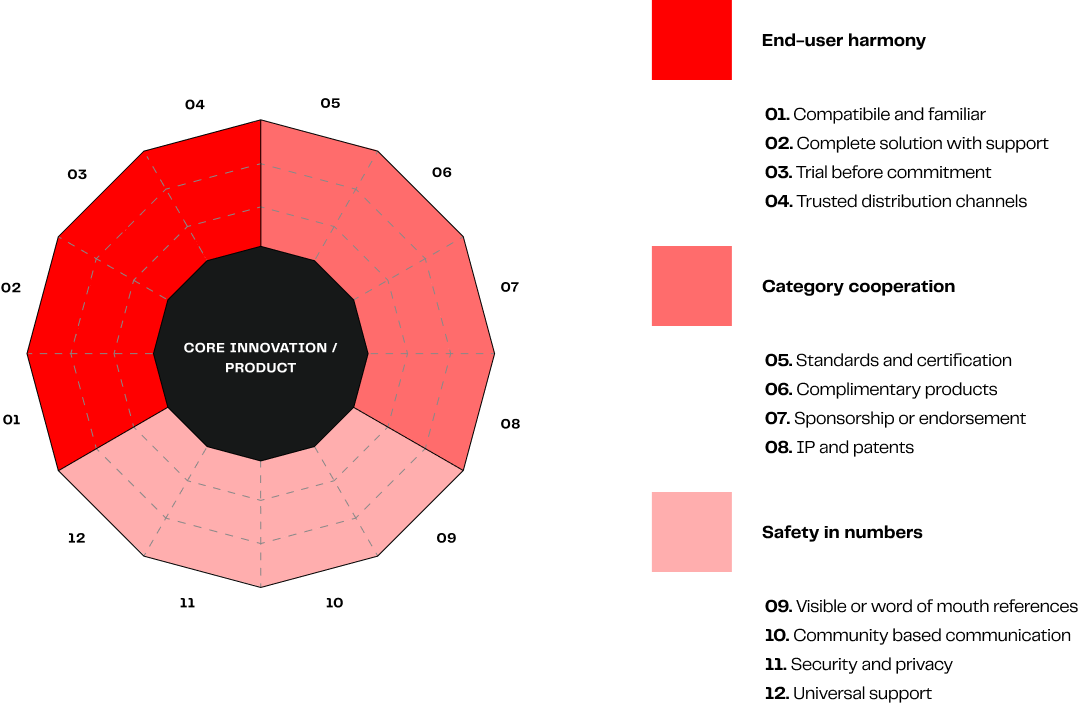
Now, we call it The Brand Differentiation Wheel™. A whole product model that helps CxO's, product managers, marketers, and product marketing managers identify the intangible brand attributes to stand out from the competition and align the value-risk reward to the requirements of the different types of technology buyers by developing these 12 elements.
We've successfully applied it as a cornerstone of the Go to Market Strategy framework in most of our +200 projects to reduce risk perception, sales cycles, and sustain growth in every stage of the product management lifecycle.
Any startup, business, and product strategy in tech that is not planning for this behavioral change in the buyers, will certainly reach a growth plateau or, even worse, fail to sustain the business.
What are the 12 drivers in technology buying decisions?
Across our projects, we have observed strong patterns on the hesitations and objections to buy of prospective buyers.
We have compiled all them and found that they fall into 12 specific attributes that buyers use to reduce the risk perception of a high-tech purchase and increase their "Perceptional Value":
1. End-User Harmony Whole Product Attributes
Buyers want harmony with their end-user. That means reduce technology adoption frictions as much as possible. These are the product completeness attributes that fall into this category:
- Compatible and Familiar: Allow users to continue using existing systems, tools, workflows, and methods as much as you can.
- Complete Solution with Support: Offering a pre-configured solution with an integrated ecosystem, plus comprehensive support.
- Trusted Channels: Allow buyers to be aware of your product and offering through their familiar and trusted distribution channels.
- Trial Before Commitment: Allow users and buyers to try your product and realize its value before committing the full investment.
2. Market Category Cooperation Whole Product Attributes
Most of the perceived value from mainstream customers, comes from the maturity of the category itself. Prospective customers want to know you category of product is not going to dissapear anytime soon, you're a credible provider within this category and you're committed to continue developing value within this category.
These are the augmented product attributes of Market Category Cooperation:
- Complimentary Products: Ensure complementary products, tools, and services are offered.
- IP and Patents
- Standards and Certification: Adhere to well-known industry standards that similar vendors work to support... or become the de-facto standard.
- Endorsements or Sponsorships: Recruit recognized organizations to support your product/innovation through sponsorships or endorsements of your market ecosystem map.
3. Safety in Numbers Whole Product Attributes
The risk-averse majority of buyers want you to proof 3rd party safeguards. This are the 4 augmented product attributes we've observed within this category:
- Universal Support: Prevent users from thinking about the technology orphans risk. Create a completely independent long-term support infrastructure.
- Security and Privacy: Prove independent safeguards that ensure both security and privacy.
- Peer-To-Peer Communication: Enable exchange of unbiased information through a user-controlled community..
- Visible or Word-Of-Mouth References: Facilitate WOM recommendations from people the user knows
and trusts.
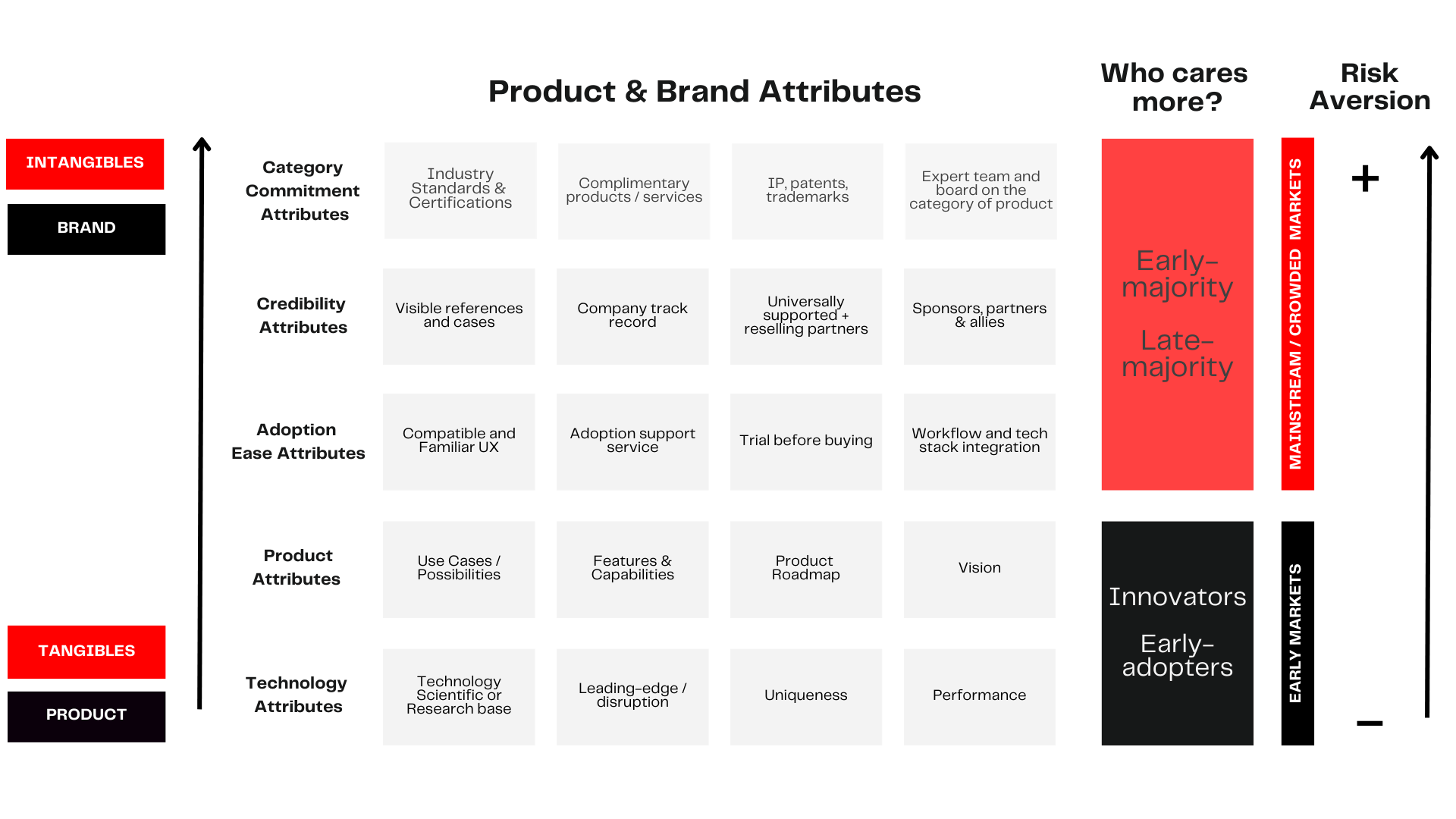
The whole product model for software-based products.
In 2023, we evolved the concept based on the patterns observed for software-based products:
About the Author

Jose M Bermejo
Founder @ The Offering Design Co - The Business Potential Strategist
CEOs call me to break revenue ceilings after burning money on ads, funnels, and hirings that did not work. I'm the call that stops the break. 15+ years in the trenches—first as a CRO scaling revenue 120%, now helping B2B CEOs stop selling harder and start selling smarter. Your "strategy" isn't the problem. Your offering is. IESE MBA. Harvard & MIT certified.
LinkedInRelated Articles
Positioning Book: The Art of B2B Tech Products Positioning
Grab a copy of the positioning book The Art of Positioning — The CEO’s Essential Guide to Strategic Market Placement for B2B Tech and Software
How to Build a Go-to-Market Strategy (That Actually Works in 2026)
Learn how to build a go-to-market strategy that works. Skip the 90-day plans—design a Gravity Offering that makes buyers say yes. Free audit.
Why Leads Don't Convert to Sales (The Two-Stage Fix Most CEOs Miss)
Why don't B2B leads convert to sales? There are only two places a pipeline breaks—and each needs a different fix. Here's how to diagnose and solve both.